Secrets of the ‘Doomsday Glacier’: The Thwaites Glacier, often referred to as the “Doomsday Glacier,” is a major player in the fight against rising sea levels. Located in Antarctica, this massive ice sheet holds enough water to raise global sea levels by over 10 feet (3 meters) if it melts completely. While that may sound like science fiction, the glacier’s rapid melting is no longer just a theoretical concern—it’s happening right before our eyes. In this article, we’ll dive deep into what scientists have discovered, how it could change the world, and what we can do to help slow down this unstoppable force of nature. Whether you’re a climate science enthusiast or someone just trying to understand what’s at stake, this guide will break down the basics and provide practical advice on how we can respond.
Table of Contents
Secrets of the ‘Doomsday Glacier’
The Thwaites Glacier is not just a scientific curiosity; it’s a ticking time bomb. As scientists work tirelessly to understand its behavior, we must pay attention to the growing evidence of its collapse. The choices we make today will determine the kind of world future generations inherit. Whether it’s through supporting climate action or making small changes in our daily lives, we all have a part to play in this global effort.

| Topic | Details |
|---|---|
| What is Thwaites Glacier? | A massive ice sheet in West Antarctica, nicknamed the “Doomsday Glacier” due to its potential to cause catastrophic sea level rise. |
| Global Impact | Thwaites’ collapse could raise global sea levels by 10 feet, threatening coastal cities and island nations. |
| Recent Findings | Scientists have discovered hundreds of icequakes and cracks in the glacier, indicating rapid instability. |
| Cause of Melting | Ocean currents and warm water are accelerating the glacier’s melt from beneath. |
| Current Efforts | International teams are working on the ground and from the air to study and understand how to slow the process. |
| How You Can Help | Simple steps, like supporting climate action policies and reducing your carbon footprint, can make a difference. |
What Makes the Secrets of the ‘Doomsday Glacier’ So Dangerous?
The Thwaites Glacier isn’t just another chunk of ice. This glacier is enormous—about the size of the state of Florida, or roughly 120,000 square miles. And it holds enough frozen water to raise global sea levels by around 10 feet (3 meters) if it melts entirely. That would be a game-changer for coastal cities around the world. Think about Miami, New York, or even places like Jakarta and Tokyo—they could be underwater.
But why is this glacier melting, and what’s causing it to speed up? Scientists have been studying this for decades, and they’ve discovered some chilling facts. Thwaites isn’t just losing ice from the top (like when snow melts), it’s also melting from beneath. Warmer ocean water is flowing under the glacier, melting it from the bottom up. This underwater melting is harder to track, but it’s responsible for a significant portion of the glacier’s loss.
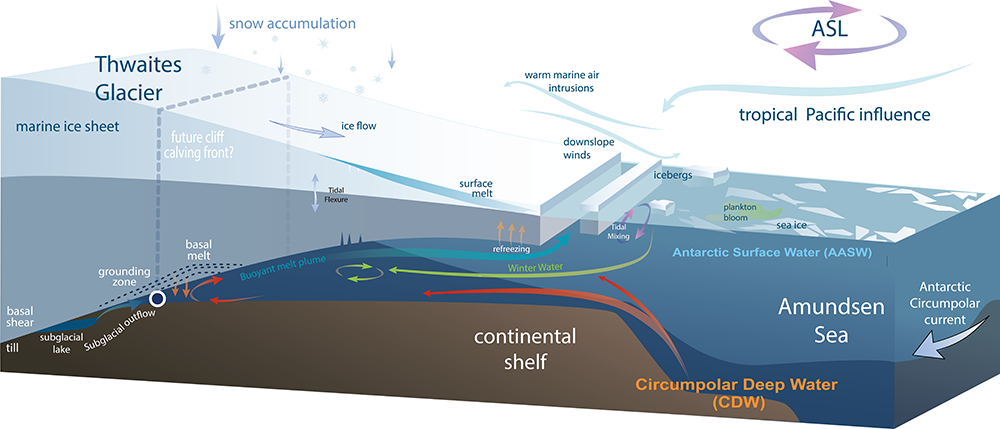
What Have Scientists Discovered So Far: Secrets of the ‘Doomsday Glacier’?
Rising Icequakes
Recently, scientists have observed a surge in icequakes—tiny earthquakes caused by the shifting and cracking of ice. These are often triggered when huge chunks of ice break off the glacier and fall into the ocean. This is a clear indicator that the glacier is destabilizing.
Key Findings
- Icequakes are increasing in frequency. These quakes show that parts of the glacier are breaking away faster than expected.
- Cracks in the ice are widening at a rate that could lead to a collapse of the entire ice shelf.
- Warm water from the ocean is getting underneath the glacier and causing it to melt from below, speeding up its demise.
Ocean’s Role in the Melting
While you might think that warming air is the main cause of the glacier’s meltdown, it’s actually warm ocean currents that are doing the most damage. As ocean waters underneath the glacier rise in temperature, they seep into cracks and crevices, eroding the ice from below. This phenomenon is speeding up the glacier’s melting process, making it even more difficult for scientists to predict how much time we have left.
Current Research and Monitoring Efforts
International teams of scientists from various countries, including the U.S. and the U.K., are closely monitoring Thwaites Glacier. These researchers are using advanced satellite technology, drilling rigs, and underwater robots to study the glacier’s movements and pinpoint the exact causes of its melting. In fact, the International Thwaites Glacier Collaboration (ITGC) has been set up to gather data from the field, and scientists are currently stationed in Antarctica, gathering firsthand information.
What Are the Main Tools in Use?
- Radar-equipped satellites to track ice shifts.
- Drones and submersible robots to measure underwater melt rates.
- Ice core samples to understand the glacier’s past behavior.
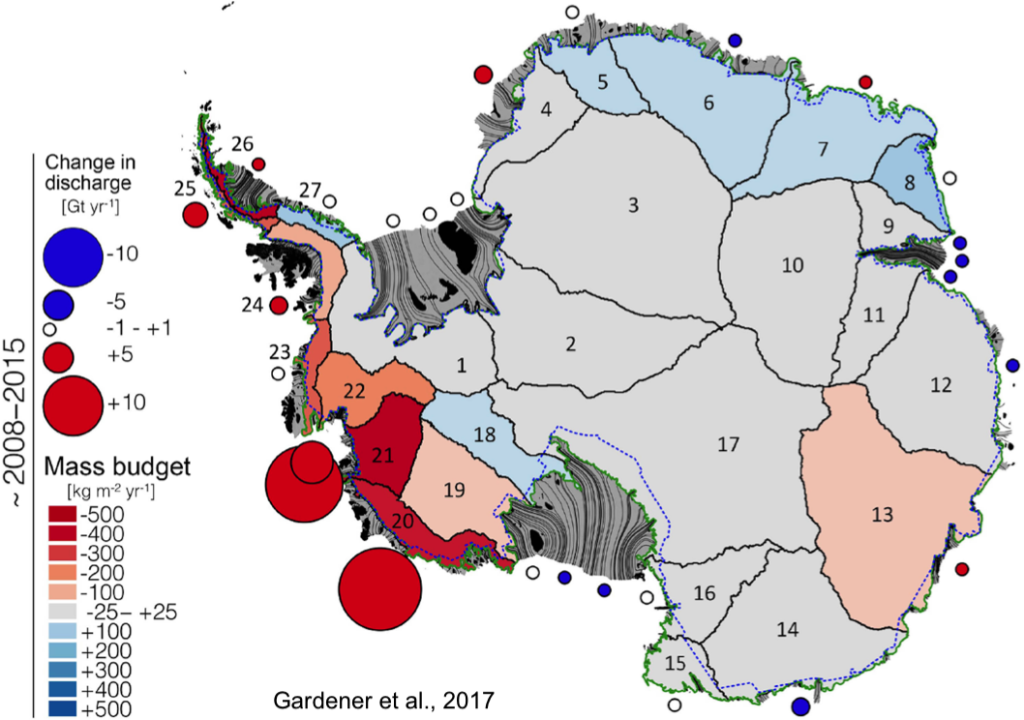
Why Should We Care About the Secrets of the ‘Doomsday Glacier’?
The impact of Thwaites Glacier’s collapse goes far beyond Antarctica. Rising sea levels would flood coastal cities, submerging low-lying islands, and threatening global infrastructure. Millions of people live in coastal areas, and many more depend on these regions for food, trade, and tourism. Thwaites holds the key to a domino effect that could trigger other glaciers to collapse.
Potential Impact:
- Coastal flooding in cities like New York, Miami, and Bangkok.
- Loss of freshwater supplies for millions of people.
- Impact on global agriculture, particularly in low-lying countries.
What Can We Do to Slow It Down?
Although it might seem like the fate of the Doomsday Glacier is sealed, there’s still hope. Scientists are racing against time to understand how to slow the glacier’s collapse and, ideally, stop it altogether. Here’s how we can play a part:
- Support Climate Action: Pressure governments to take action on climate change. Reducing global emissions and switching to renewable energy sources can slow the warming process.
- Reduce Carbon Footprint: Individuals can cut down on waste, use energy-efficient appliances, and opt for sustainable products.
- Support Scientific Research: Donating to organizations working on glacier research and conservation efforts can help fund the tools and studies that could save our world.
This New Glue Is So Strong It Can Tow a Car; Scientists Say It Could Replace Welding
FAA Issues Emergency Alert: SpaceX Debris Forces Sudden Flight Path Changes Across the U.S.
Goodbye, Traditional Motorcycles: Kawasaki Corleo Redefines the Future of Two-Wheeled Mobility