Goodbye to industrial beauty gummies: that’s the new skin-savvy mantra echoing from the healthy kitchens of Los Angeles to the ancestral hearths of Indigenous America. People are turning away from overpriced, sugary skin supplements and looking inward—literally—toward natural, nourishing foods like carrots and bone broth to get that radiant glow. This movement, sometimes trending under the name “edible retinol,” is not just a fleeting TikTok hashtag. It’s a powerful return to ancestral knowledge and common-sense nutrition—backed by science. In this guide, we’re diving deep into what edible retinol really is, the real science behind it, and how to use foods to fuel your skin from the inside out.
Table of Contents
Goodbye to industrial beauty gummies
Saying goodbye to industrial beauty gummies isn’t just a diet trend—it’s a smart, science-backed return to food-based skin care. By eating beta‑carotene-rich vegetables and collagen-boosting broths, you support your body’s natural glow with time-tested, nourishing choices. Food has always been our first medicine. So next time you reach for that sugar-packed beauty chew, remember: your skin might just prefer a warm bowl of broth and a roasted carrot instead.

| Topic | Summary |
|---|---|
| What is Edible Retinol? | A nutrition-based skincare concept using foods high in beta‑carotene and collagen-boosting compounds. |
| Best Foods | Carrots, bone broth, sweet potatoes, spinach, pumpkin, bell peppers. |
| Industry Trend | Beauty gummies industry projected to grow from $4.3B in 2025 to $38.8B in 2035. |
| Bone Broth Surge | Bone broth market forecasted to reach $1.62B by 2030. |
| Nutrient Synergy | Real foods offer a full nutrient matrix for holistic skin health, unlike isolated supplements. |
Why People Are Ditching Industrial Beauty Gummies?
Beauty gummies—those pastel-colored, candy-like chews—promise everything from youthful skin to luscious locks. But behind the cute packaging lies a cocktail of sugar, dyes, and fillers. In fact, most over-the-counter gummies contain low concentrations of bioavailable nutrients, and some are downright gimmicky.
It’s no wonder that informed consumers are looking toward whole food-based nutrition to support their beauty goals. Whether it’s rooted in ancestral food practices, a push against ultra-processing, or simple common sense—real food is making a comeback.
Not to mention, your skin is your largest organ. It reflects your internal health. That’s why what you eat matters just as much—if not more—than what you slather on your face.
What is Edible Retinol (Really)?
Despite the buzz, edible retinol is not actual retinol. Let’s clear that up. Retinol is a synthetic derivative of vitamin A, commonly used in topical skincare to treat acne, pigmentation, and signs of aging. It’s potent—and can be irritating.
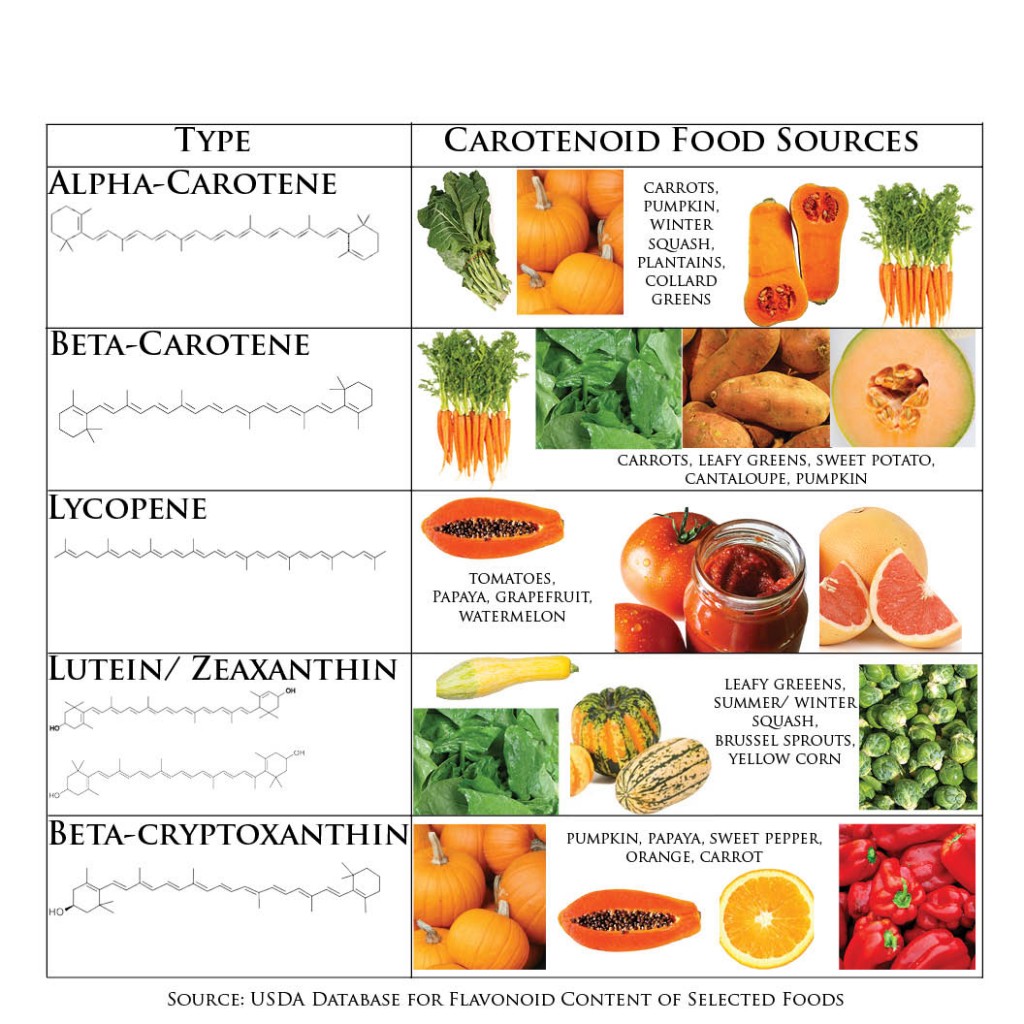
What we call “edible retinol” is actually beta‑carotene, a plant-based compound that the body converts into vitamin A when needed. Think of it like your body’s vitamin A safety net. When consumed through food, beta‑carotene gives your body the tools to create retinol on demand, but at safer, regulated levels.
According to the NIH, beta-carotene is a provitamin A carotenoid, meaning it’s a precursor your body converts into active vitamin A (retinol) when needed — without the risk of toxicity from overconsumption of supplements.
That’s a major benefit. Unlike high-dose retinol supplements or creams, your body only takes what it needs from beta‑carotene, making it gentler and safer for daily use.
Goodbye to industrial beauty gummies: Top Foods That Act Like Edible Retinol
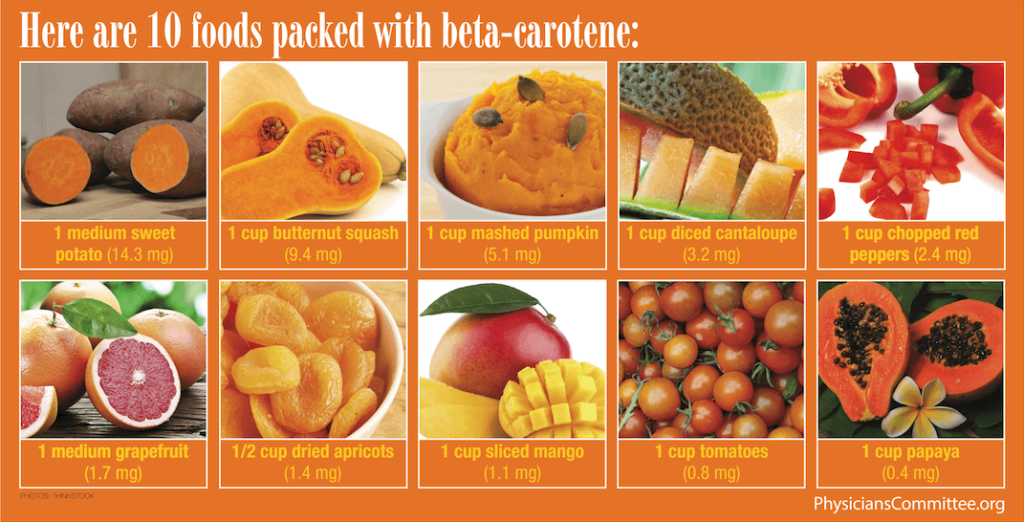
These foods are rich in beta‑carotene and other nutrients that support skin structure, collagen formation, and antioxidant protection:
1. Carrots
One of the richest sources of beta‑carotene. One medium carrot provides over 500% of your daily vitamin A needs.
2. Sweet Potatoes
Even more powerful than carrots. A single medium sweet potato has 1,096 mcg of retinol activity equivalents (RAE).
3. Pumpkin & Winter Squash
Seasonal powerhouses loaded with skin-boosting beta‑carotene.
4. Spinach & Kale
These leafy greens provide both beta‑carotene and lutein, another antioxidant tied to healthy skin and eyes.
5. Red Bell Peppers
High in vitamin C and beta‑carotene—essential for collagen synthesis and skin repair.
6. Bone Broth
While it doesn’t contain beta‑carotene, it’s rich in collagen, glycine, and proline—key for skin elasticity and hydration.
According to Harvard’s T.H. Chan School of Public Health, dietary beta‑carotene absorption increases when paired with healthy fats like olive oil or avocado.
Bone Broth: The Unsung Hero of Skin Health
Bone broth deserves its own spotlight. Traditional cultures—Native American, Mexican, Asian, and many others—have long used bone broth for its healing properties. Today, science backs those traditions.
Simmering bones for hours pulls out:
- Collagen – foundational for skin’s structure.
- Gelatin – helps skin retain moisture.
- Amino acids – like glycine, proline, and glutamine, which aid tissue repair.
A 2021 study in the Journal of Clinical Nutrition linked collagen-rich diets with improved skin elasticity, hydration, and dermal collagen density—all things beauty products promise but can’t guarantee through external use alone.
Retinol vs. Beta‑Carotene: Side-by-Side Comparison
| Category | Topical Retinol | Edible Beta‑Carotene |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Synthetic | Plant-based |
| Route | Absorbed via skin | Absorbed via digestion |
| Function | Wrinkle reduction, acne | Skin support, immune health |
| Strength | High, can irritate | Moderate, body-regulated |
| Risk | Can cause dryness, redness | Low toxicity from food |
Conclusion: You don’t have to choose. Topical and dietary forms of vitamin A can complement each other when used wisely.
The Ancestral Nutrition Connection
This isn’t just about ditching gummies. It’s about reconnecting with ancestral wisdom.
Indigenous diets across Turtle Island (North America) were deeply rooted in seasonal, nutrient-dense, local foods like:
- Root vegetables (carrots, beets, yams)
- Wild greens (dandelion, stinging nettle)
- Broths from hunted game
- Seeds and nuts high in essential fatty acids
These foods provided everything needed for robust health, clear skin, and long-term vitality—without a single synthetic pill.
Bringing these foods back into your diet isn’t just good for your skin—it’s a reconnection to culture, land, and real nourishment.
How to Eat for Glowing Skin: A Daily Plan
Here’s a sample one-day guide to support your skin with edible retinol ingredients:
Morning
Golden Glow Smoothie
- 1 steamed carrot
- ½ banana
- ½ cup Greek yogurt
- Dash of cinnamon
- 1 tsp flaxseed oil
Packed with beta‑carotene and healthy fat for absorption.
Lunch
Bone Broth Veggie Soup
- 2 cups bone broth
- ½ cup chopped sweet potato
- Handful of kale
- Garlic, turmeric, and sea salt
Combines collagen support with beta‑carotene greens.
Dinner
Roasted Veggie Bowl
- Roasted carrots, red peppers, and butternut squash
- Served over quinoa or wild rice
- Drizzle of olive oil and lemon juice
Balanced, nourishing, and skin-supportive.
Snack
Pumpkin-Hummus Dip
- ½ cup canned pumpkin
- ¼ cup tahini
- Garlic and cumin
Great with cucumber or carrot sticks.
Welcome to the Bizarre Lemon-Shaped Planet Where It Literally Rains Diamonds Inside
It’s Official: 2026 Will Feature 13 Full Moons, 3 Supermoons & a Rare Blue Moon Spectacle
Goodbye to 24-Hour Days? NASA Warns Earth’s Rotation Is Speeding Up—Time Itself May Be Changing